How to steward security in your remote workplace. #CyberPandemic.

Marc Chataigner
UX DesignAs a simple metric, the FBI has seen a fourfold increase in cybersecurity complaints. At the same time, the global losses from cybercrime exceeded $1 trillion in 2020.
The world post-2020 isn't quite the same. While the digital transformation is accelerating, executives still need to figure out ways to secure their digital assets and teams.
2021 PwC survey on CEOs says: "remote working makes cybersecurity a top worry."#
The PwC underlines that focusing security efforts on risk dashboards, surveillance and technical initiatives remains tempting. CEO and CISO know how to account for those investments.
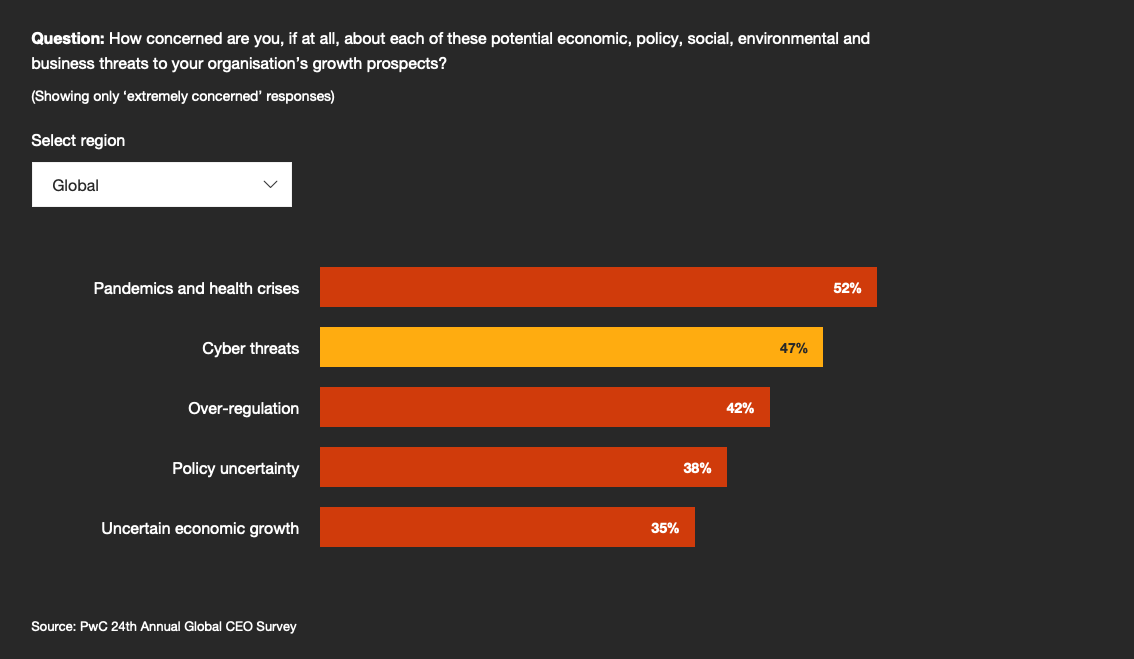
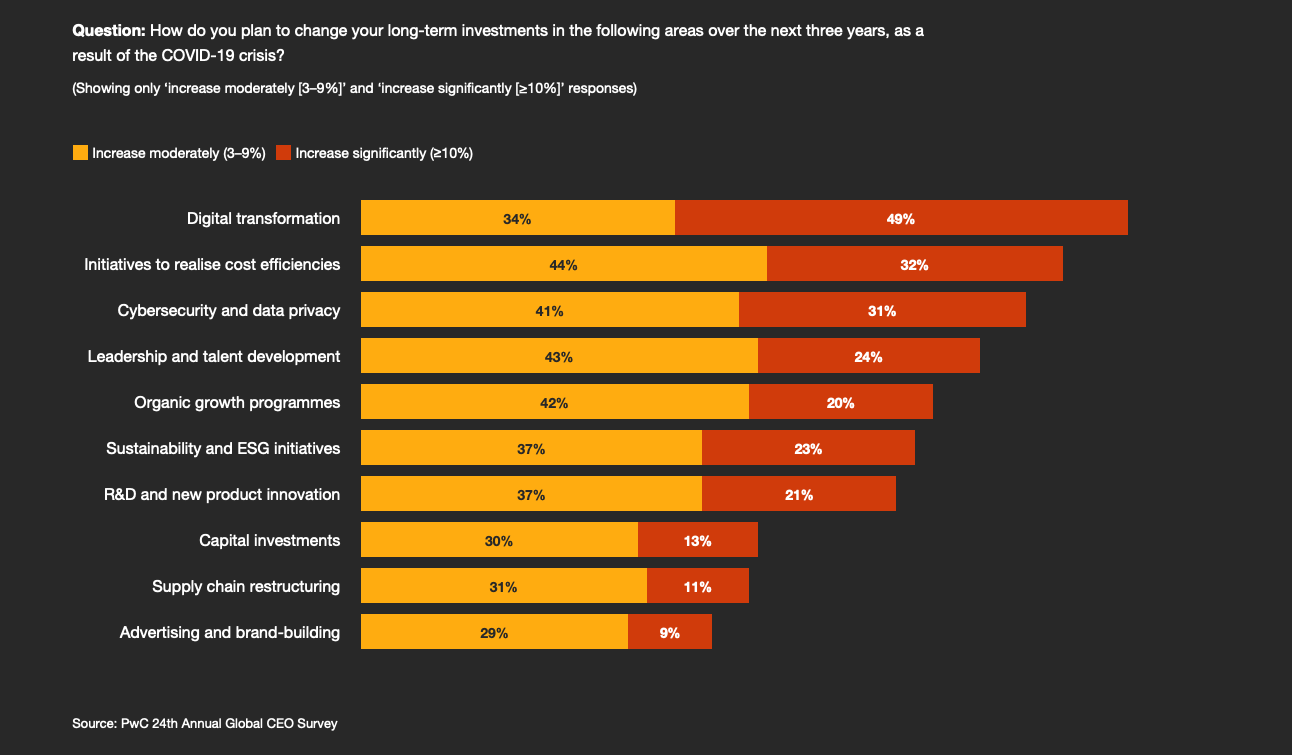
According to PwC, around half of CEOs plan increases of 10% or more in their long-term investment in digital transformation. Paradoxically, despite the level of concern CEOs registered about cyberattacks, just under half of those planning for heightened digital investment is also planning to boost their spending on cybersecurity and data privacy by 10% or more.
The PwC report stresses that "leaders who are serious about cybersecurity need to embrace simplicity in their strategic dialogue about their business models, ecosystems and in-house processes".
Read more about the PwC 2021 report.
A look at the five biggest cybersecurity threats in 2021:#
As cyber threats become sophisticated, it becomes illusory to think that a technical fix would do the job. People, teams, management, and suppliers, customers, every node of the network ought to be onboarded.
Security Magazine builds down the five cybersecurity risks as:
- Social engineering - Social engineering techniques account for a third of all breaches in 2020. 90% of social engineering hack is based on phishing. Spear phishing attacks are behind 95% of breaches in enterprise networks, according to Cisco.
- Ransomware - In 2020, combined ransomware demands reached $1.4B. Ransomware ranks as the third most popular malware causing data breaches.
- DDoS attack - Just for the first half of 2020, there were 4.83M DDoS attacks attempted. Besides increasing traffic, cybersecurity experts stress that criminals use AI to perform DDoS. Remote workforces became highly dependent on online services. Any failure of those may cost even more to businesses.
- 3rd party software - Besides hammering your business reputation, the data breach caused by a third party costs $4.29M on average. The third-party vendor ecosystem becomes a pool of vulnerabilities.
- Cloud Computing Vulnerabilities - while the cloud computing market keeps growing rapidly, the attempted breaches grew by 250% compared to 2019. Cloud systems are also critical components of DDoS attacks.
Read more about it on Security Magazine.
Keep in mind, employees are not the same at home#
To delve further into corporate security solutions, CISO Jonathan (Jony) Fischbein has inspiring words. One of the main point to bear in mind is that "employees are not the same" when they are at home. Not only because of mixing professional and private time-spaces, their mental awareness, work implication, or feeling of security are different from the days they have badged to enter their office.
"Nobody is looking" when we work from home. Internet accesses or multitasking practices are not to ban or forbid. But we shall bear in mind that they add a fair amount of risk to your organization.
Jony Fischbein coins these times as "Pandemic Security" times.
More on Cyber Talk.
So here is what to protect, and when.#
Experts gathered by Sloan note that cybersecurity is shifting away from a perimeter-based model where all assets inside a network are trusted. Instead, zero-trust architectures, where individual devices and applications are always authenticated and authorized before gaining access to a network, need to become the norm.
Regarding digital assets to care for, consider:
- identities and credentials
- data, in its different states (at rest, in move, in use)
- code
As for exposure points, consider:
- storage
- run-time
- transfer
Continue reading the details on Security Magazine.